Discovering the Elephant Pitcher Plant: A Unique Carnivorous Wonder
October 29, 2024The Elephant Pitcher plant, also known as Nepenthes rajah, is a truly remarkable species of carnivorous plant native to Borneo. Its massive pitchers, resembling the shape of an elephant’s ear, have captivated botanists and nature enthusiasts for centuries. This article delves into the fascinating world of the elephant pitcher, exploring its unique characteristics, habitat, and the intriguing ways it captures its prey.
The Giant of the Pitcher Plant World
The elephant pitcher plant earns its name from its enormous pitchers, which can grow up to 41 cm high and 20 cm wide. These impressive traps are capable of holding up to 3.5 liters of digestive fluids, making them some of the largest in the carnivorous plant kingdom. The pitchers are typically reddish-purple in color and possess a distinctive lid, or operculum, that helps to prevent rainwater from diluting the digestive enzymes within.
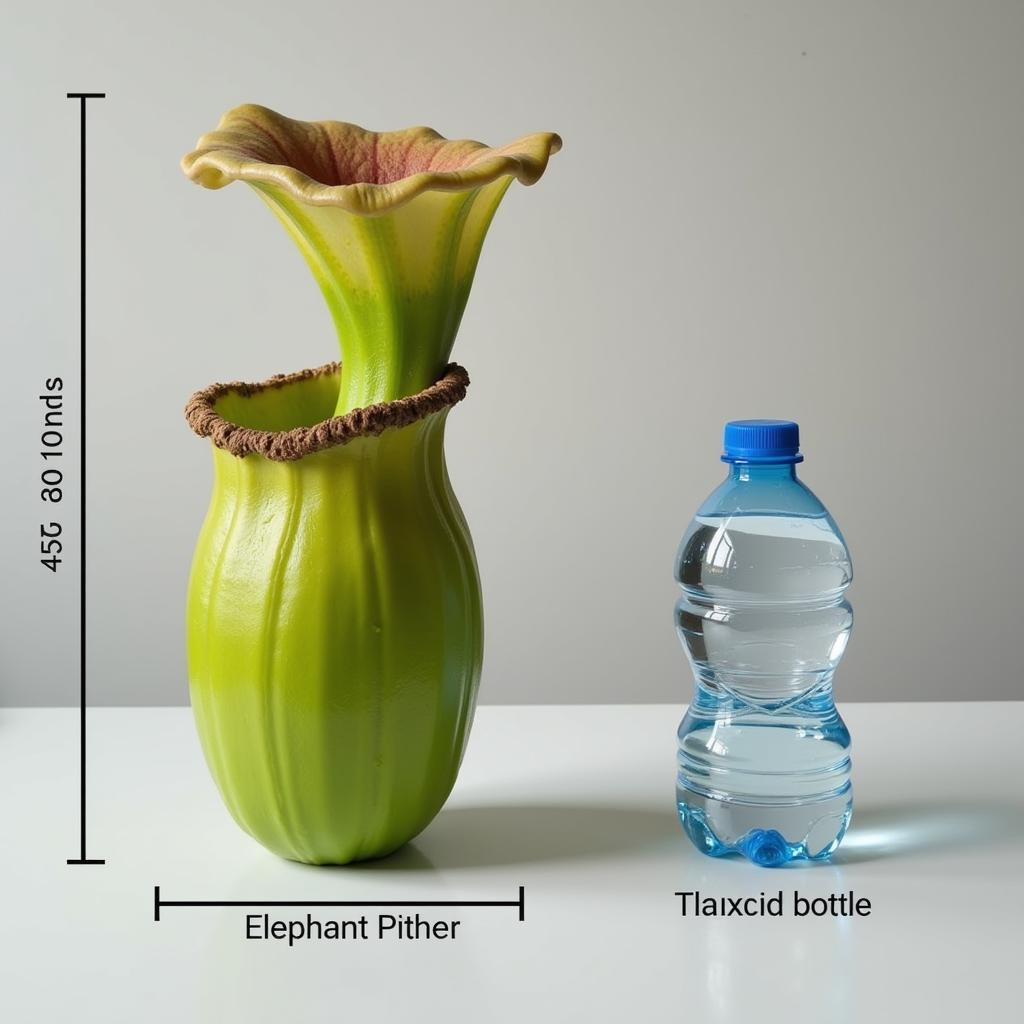 Elephant Pitcher Plant Size Comparison
Elephant Pitcher Plant Size Comparison
What makes the Nepenthes rajah even more fascinating is its unique relationship with certain small mammals. While primarily known for trapping insects, the plant’s sugary nectar also attracts tree shrews and summit rats. These animals use the pitcher as a toilet, providing the plant with valuable nitrogen-rich feces. This symbiotic relationship highlights the intricate connections within the rainforest ecosystem.
Habitat and Conservation Status
The elephant pitcher plant is endemic to Mount Kinabalu and Mount Tambuyukon in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. It thrives in high-altitude, mossy forests where the soil is nutrient-poor. This challenging environment has led the plant to evolve its carnivorous habits, allowing it to supplement its nutrient intake by trapping and digesting prey.
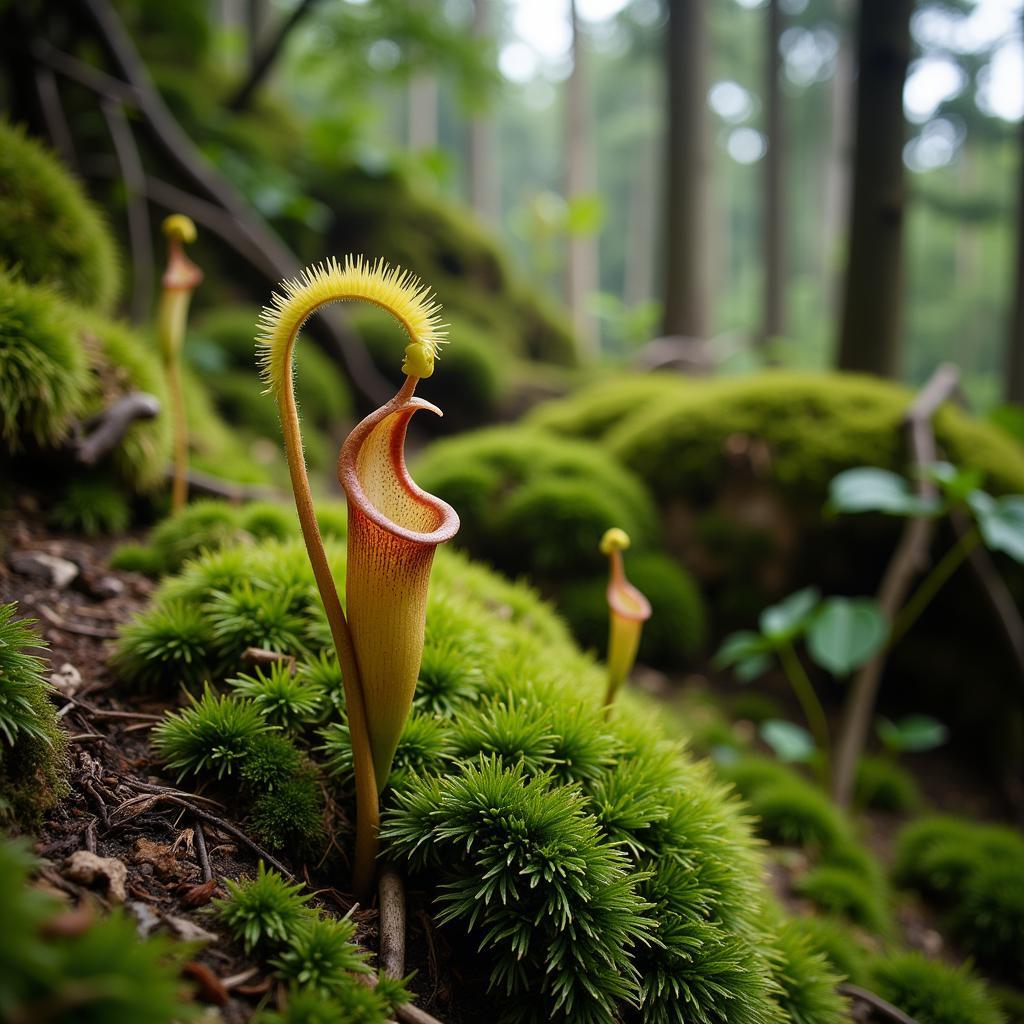 Elephant Pitcher Plant in its Natural Habitat
Elephant Pitcher Plant in its Natural Habitat
Unfortunately, the elephant pitcher plant is classified as endangered due to habitat loss, poaching, and the illegal plant trade. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect this extraordinary species and ensure its survival for future generations. Organizations are working to protect the plant’s natural habitat and raise awareness about its importance.
How the Elephant Pitcher Traps Its Prey
The elephant pitcher plant employs a passive trapping mechanism. The pitchers are lined with a slippery coating of nectar, which attracts unsuspecting insects and other small creatures. Once an insect lands on the rim, it loses its footing and slides down into the pitcher’s depths. The pitcher’s interior is filled with digestive fluids containing enzymes that break down the captured prey, providing the plant with essential nutrients.
 Elephant Pitcher Plant Trapping Mechanism
Elephant Pitcher Plant Trapping Mechanism
“The Nepenthes rajah is a true marvel of evolution,” says Dr. Amelia Tan, a botanist specializing in carnivorous plants. “Its ability to adapt to such a harsh environment and develop such a sophisticated trapping mechanism is truly remarkable.”
Another expert, Dr. David Lee, adds, “Conserving this unique species is not just about preserving a single plant; it’s about protecting the biodiversity of the entire rainforest ecosystem.”
Conclusion
The elephant pitcher plant, with its giant pitchers and unique symbiotic relationships, stands as a testament to the wonders of the natural world. Understanding and protecting this endangered species is crucial for preserving the biodiversity of our planet. Let us continue to marvel at the elephant pitcher and support efforts to ensure its survival for generations to come.
FAQs
-
What is the largest pitcher plant in the world?
The Nepenthes rajah is considered the largest pitcher plant in the world based on the volume of its pitchers. -
Where does the elephant pitcher plant grow?
The elephant pitcher plant is endemic to Mount Kinabalu and Mount Tambuyukon in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. -
Why is the elephant pitcher plant endangered?
Habitat loss, poaching, and the illegal plant trade are the main threats to the elephant pitcher plant. -
How does the elephant pitcher plant trap its prey?
The plant attracts prey with nectar and traps them in its slippery pitchers filled with digestive fluids. -
What is unique about the elephant pitcher plant’s relationship with mammals?
Certain small mammals use the plant’s pitchers as toilets, providing the plant with valuable nutrients. -
What color are elephant pitcher plants?
They are typically reddish-purple. -
How big can an elephant pitcher plant grow?
The pitchers can grow up to 41 cm high and 20 cm wide.
You may be interested in Yankees jersey Mariano Rivera.
For further assistance, please contact us: Phone: 0963418788, Email: [email protected] or visit our address: 2M4H+PMH, Phường Nghĩa Thành, Gia Nghĩa, Đắk Nông, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.